2016.10.03 update
K computer Able to Determine Important Fullerene Properties-Scientists employ the supercomputer and quantum chemistry calculations to accurately predict the material’s heat of formation-
Researchers at RIKEN harnessed the power of the K computer to successfully compute a basic property—the heat of formation—of 10 fullerene molecules: a C60 molecule (60 carbon atoms) and nine higher-order molecules (each consisting of more than 60 carbon atoms).*1 Heat of formation is a measure of the energy released or consumed when one mole of a substance is created from its pure elements and is a major identifier of a material’s properties.
Building on this knowledge, the researchers then hypothesized on why the physical properties of the two kinds of carbon allotropes, fullerenes and graphene, are so different. They were also able to predict how enlarging the fullerene molecules affect their physical properties.*2 These results will help provide a basis for application development of the fullerenes.
Fullerenes show great promise for innovative applications in a range of fields, including medicine, electronics, nanotechnology and cosmetics. RIKEN’s findings are expected to open the way for new material-design work based on computational science.
*1…The nine higher-order fullerenes are C70, C76, C78, C84, C90, C96, C180, C240 and C320, the numerals indicating the number of carbon atoms composing each fullerene. *2…In related research projects, the scientists are investigating the superconductivity that occurs when an atom of an alkaline metal is inserted into a C60 fullerene molecule, and research is also being carried out on higher-order-fullerenes, whose hollow center sizes enlarge as the number of carbon atoms increase.
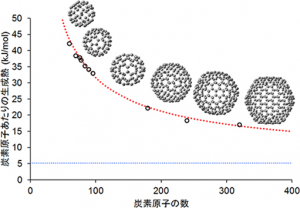
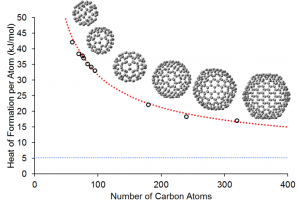
The vertical axis shows the heat of formation for each carbon atom in a fullerene molecule. The small circles show the results of RIKEN’s calculations for the 10 fullerenes molecules. The red-dotted line depicts the formation of heat for the fullerenes calculated using a general theoretical formula for computing the formation of heat for larger fullerene molecules that is derived from RIKEN's research. The blue-dotted line indicates graphene’s heat of formation, as measured in past experiments.
- Related Links:
-
RIKEN (Press Release)
RIKEN (Riken Research Highlight)